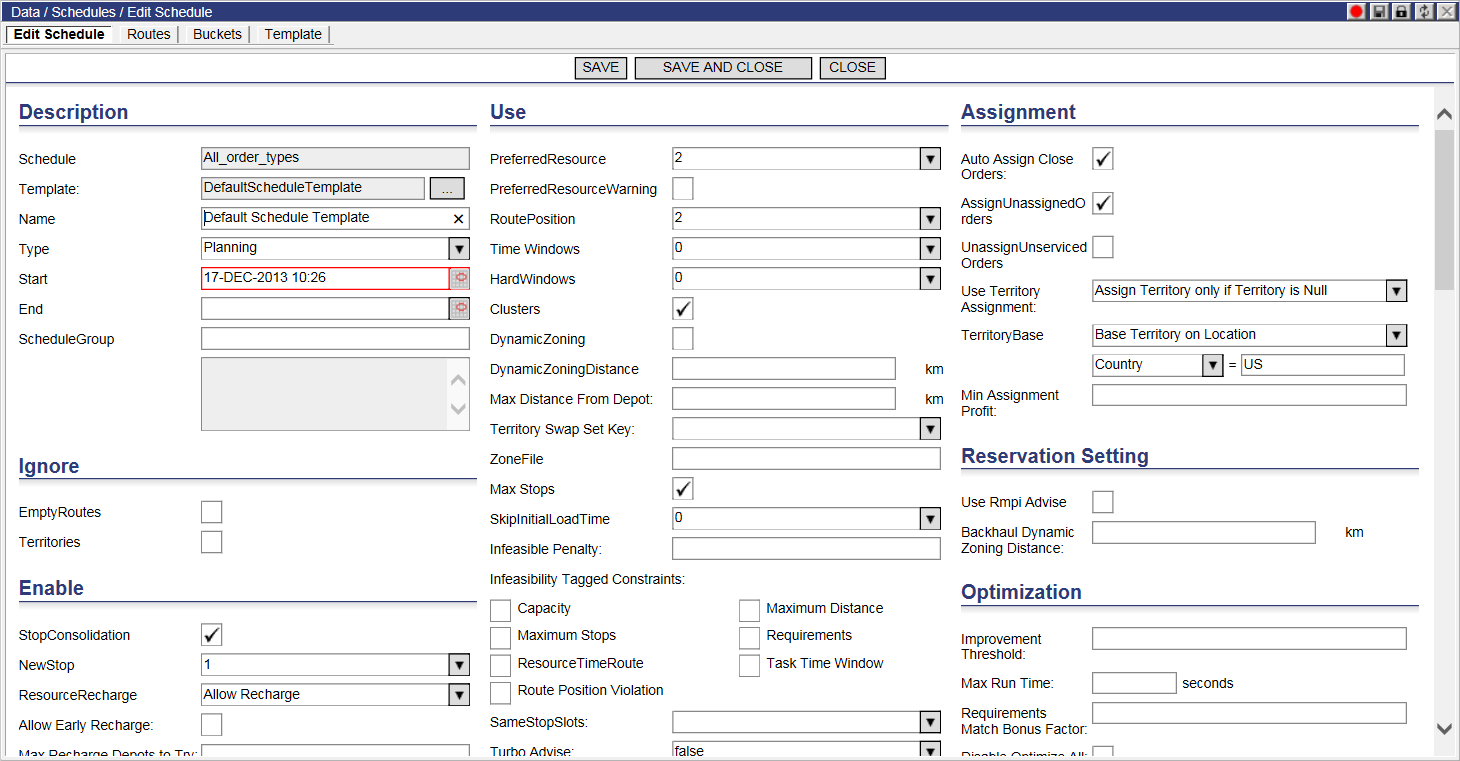
To view and edit the details of a Schedule:
1 Double-click the desired Schedule, or from the Schedules list, right-click on the desired Schedule and select: Edit.
The Edit Schedule page appears:

2 To edit, modify or add data in the appropriate fields (see below for more detail on each section and field).
3 When finished entering data, click Save.
Ü Note&emdash; Any settings changed and set in the User Interface (UI) takes precedence over the same settings in other places such as the database and rimpi.ini file. These settings are stored in the FWSchedule table. If any fields are left as NULL, then values and settings are taken from the rimpi.ini file. If no values are in the UI or Rimpi then the defaults are assumed.
All time values in the LNOS database are set in seconds. LNOS will convert the data into the correct format for Rimpi automatically.
Apply section
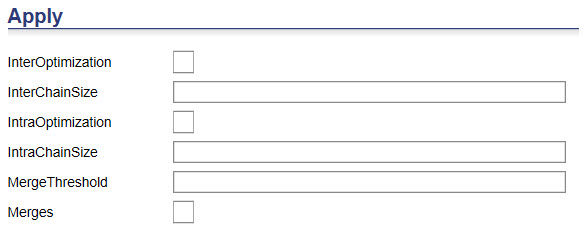
InterRoute Optimization - InterRoute Optimization moves jobs between routes. It consists of three steps:
1 The Optimizer examines each pair of routes to find chains (or sequences) of jobs that can be moved between two routes.
2 The Optimizer attempts to merge routes, by adding one route to the end of another.
3 If different resources have different cost structures, the Optimizer attempts to exchange entire routings between resources to find the most efficient assignment of resource to routing.
IntraRoute Optimization - IntraRoute Optimization moves jobs within a single route. The Optimizer examines each route to find chains (or sequences) of jobs that can be moved within the route to create an efficiency improvement.
Chain size - The recommend/standard figure here is four. The larger the chain size the longer the optimization takes because it has more combinations of jobs to try and move. Therefore it depends how quickly you want the optimization to finish. If you are after the best possible quality and have no time constraint increase its size.
Merges - Determines if the Optimizer attempts to merge routes or not. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), the Optimizer will attempt to merge two routes if the resulting route would have a total length less than MergeThreshold. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will not attempt to merge routes.
The default is false (unchecked). Merging should only be used when routes are small.
Ü Note&emdash; The majority of customers have merging turned off. For Descartes Routing and Scheduling users using the BGO this setting doesn’t matter; the BGO effectively tries merging in its Inter/Batch Assign phase where it takes a group of compatible routes, unassigns all the jobs from them and then batch assigns them back onto the same routes.
MergeThreshold - Maximum route length that can be created by merging two routes. See Merges above. This is recommended when you have an expected number of stops for a resource.
The default is zero (0). When set to zero, the Optimizer will not attempt to merge routes. Merging should only be used when routes are small.
If a job needs to stay on the current day it is on see note below:
Ü Note&emdash; An inter optimization tries to improve the quality of the routes and remove violations. Moving a job to a route to the wrong day would put it in violation so it is extremely unlikely to do that. The only reason it might possibly do that is if the job was already missing its time window and the cost and penalties that are being used make it incur less penalties by moving it to another day. Generally if a job can’t be serviced during its time window then the optimizer will put it on a route such that it incurs the least penalties and cost. So when determining the costs and penalties for an implementation, you need to decide what you want to happen if a job can’t be serviced in its window. Should it be placed on a route so that it is as close to its time window as possible or should it be placed next to a job at a close by location. This is determined by either making mileage costs high or the MissedTimeWindowPenalty high.
Limits
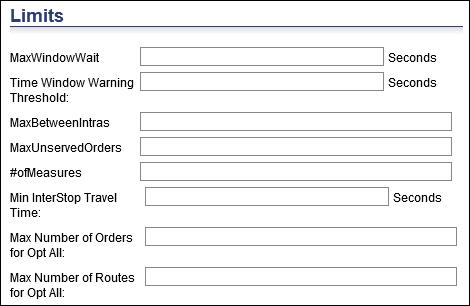
MaxWindowWait - This is ideally used for batch optimizations to determine how long a resource can wait outside a customer location for the time window to open. If you are not using batch processing and using reservations then this figure needs to be set to the length of the longest route. If using batch processing, then a good figure would be twenty minutes, if using reservations leave blank, this will then default to twenty-four hours.
For example, you may have a window for a resource from 7:30am till 5pm. If one job is put on the resource for a 2-4 time window and your max window wait is twenty minutes, then a violation will be occur.
MaxBetweenIntras - When non-zero, during the Assignment Process, the Optimizer runs an IntraRoute Optimization pass every time the specified number of jobs is assigned to a route. For example, if the setting is ten, IntraRoute Optimization runs after the Optimizer has assigned ten jobs, twenty jobs, thirty jobs, and so on.
The default is zero.
Ü Note&emdash; If you have a tightly constrained problem, such as narrow time windows or capacity constraints, using this setting can help generated better assignment answers because it slows down the Assignment Process.
MaxBetweenIntras - Having this set to zero makes optimizations take longer but can give better results. All jobs still get assigned.
MaxUnservedOrders - The maximum number of unserved jobs that can be assigned. A value of -1 places no restriction on unserved jobs.
The default value is -1 (no restriction on unserved jobs).
Ü Note&emdash; This is an approximate setting. Under certain conditions generally related to cost structure, the Optimizer can assign more unserved jobs.
There has never been a case where this has not been set to -1.
# of Measures - This is the schedule setting NumMeasures. It is important to set this correctly. If you are using two measures and have this set to one then the optimizer will ignore the second measure. You can have up to nine measures. For example, if you have five measures and this value is set to three, it will only use the first three measures.
Min InterStop Travel Time &endash; Allows users to enter a minimum value for the travel time to be used between two GeoStops. If RMPI calculates the travel time of a route between GeoStops and the resulting time value is less than the entered Min InterStop Travel Time, the Min InterStop Travel Time is used instead.
Max Number of Orders for Opt All &endash; Allows users to set a maximum number of assigned and unassigned orders to be sent to RMPI via Optimize All. If a set of orders exceeds the set maximum, the system returns a warning message.
Max Number of Routes for Opt All &endash; Allows users to set a maximum number of routes to be sent to RMPI via Optimize All. If a set of routes exceeds the set maximum, the system returns a warning message.
Restrict

Viable Orders - RestrictToDoableJobs. Generally this should be set to on. If a job is not doable; its measures exceed the capacity of all resources. For example, if no resource is working during its delivery window, then the optimizer will ignore it and not waste time trying to assign it.
Zonable Orders - Determines if the Optimizer assigns jobs with a territory. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then only jobs that have a territory will be assigned. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer performs the following tasks:
1 assigns all jobs that have a territory
2 tries to assign the rest of the jobs
The default value is false (not checked).
Ü Note&emdash; To prevent violations caused by the Optimizer from occurring set the Zoneable Orders setting to true.
Swap to Neighbors - Limits InterRoute Optimization to swapping between routes that are in close proximity. This may improve the Optimizer’s performance. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer will only examine pairs of routes that are close together. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will examine all pairs of routes subject to zone definitions.
The default value is false (not checked).
Ü Note&emdash; This should be set to true (checked) if the zones are not well-defined. Otherwise you might miss swap opportunities if capacities are included.
Swap to Points - Limits InterRoute Optimiziation to swapping jobs that are in close proximity. This may improve the Optimizer’s performance. This should only be used if ”Error! Reference source not found.” is set to true (1). If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer will only examine pairs of jobs that are close together and on neighboring routes. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will examine all pairs of jobs.
The default value is true (checked).
Ü Note&emdash; If the value is not true, then you might miss swap opportunities if capacities are included.
Swap Within Territory - Determines if the Optimizer limits job swapping to within territory. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then job swapping is limited to same territory only. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0) then job swapping is controlled by the [Swaps] section of the zone file.
The default value is false (unchecked).
Optimization
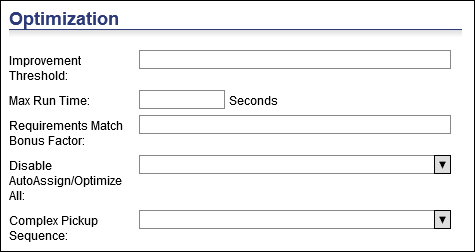
Improvement Threshold - During the Improvement Process, the Optimizer will not consider any route change if the net profitability improvement is smaller than this number. The default setting of approximately 0.1 allows the Optimizer to find improvements that save miles while ignoring changes that save feet.
Ü Note&emdash; Smaller numbers may mean longer run times.
Max Run Time - This setting is defined in seconds and allows users to specify a maximum running time for an optimization run.
Requirements Match Bonus Factor &endash; Multiplier ranging between 0 and 1 which, when multiplied to an order’s profit, produces a bonus profit to be added to a route profit. The bonus gets effective only when the order’s requirements are met by the resource’s capabilities. Default is 0.01.
Disable AutAssign/Optimize All &endash; This setting has two options.
• Disable Optimize/AutAssign All: When selected, the Optimize All and Auto Assign All options will be hidden from right-click menus.
• Disable Optimize/AutAssign All/Selected: When selected, the following options will be hidden from right-click menus:
• Optimize All
• Auto Assign All
• Optimize Selected on the Unassigned Stops quadrant
• Optimize Selected, when more than one non-frozen routes are selected on the Route Summary page or Route Detail quadrants
• Optimize Selected, when multiple unassigned stops are selected on the map or multiple non-frozen routes are selected on the Map quadrant
• Auto Assign on the Unassigned Stops quadrant or when multiple unassigned stops are selected on the Map quadrant
Complex Pickup Sequence &endash; This field allows users to specify to RMPI the sequence of pickups for double-ended jobs at the same depot based on the delivery sequence:
• null: Last in, first out (LIFO)
• 1: Last in, first out (LIFO)
• 2: First in, first out (FIFO)
Suggest

Max Suggestions - Max Number of Suggestions to be returned during a suggest call.
Max Suggests Per Route - Max Number of suggests returned per route.
Max Suggests Per Day &endash; Max Number of suggests returned per day.
![]() Note&emdash;
These settings apply to both the Suggest
and Suggest Order functions.
Note&emdash;
These settings apply to both the Suggest
and Suggest Order functions.
Ignore

Empty Routes - Determines if resources without assigned jobs are considered during inter-route swapping. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer will only consider resources that already have jobs assigned. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will consider all resources.
The default value is false (not checked).
Ü Note&emdash; This setting is ignored during the Assignment Process.
Territories - Determines if territories are ignored. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then territories will be ignored. If the box is unchecked (false &endash; 0), then territories will be used.
The default is zero.
Enable
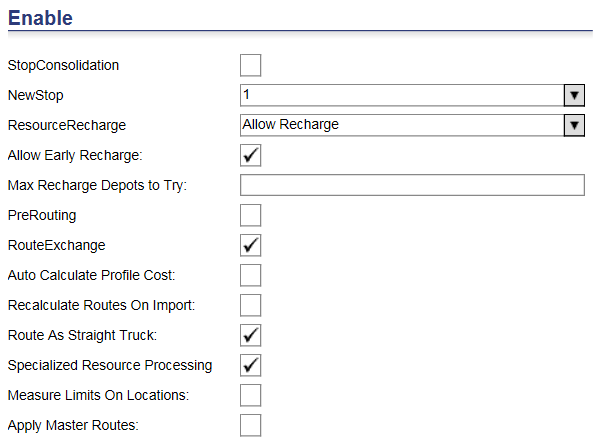
Stop Consolidation - Determines the Rmpi handling of multiple jobs for the same stop (see NewStop) with identical time window constraints. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then servicing the first job in the group implies that all jobs for the same stop are serviced successfully. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then each distinct job is evaluated against its distinct job is evaluated against its distinct EarliestTime/LatestTime window (or Open/Close) constraints for success or failure in servicing.
New Stop - Determines what represents a stop in Rmpi and Stop Numbering in Schedule. The values are:
· 0 &endash; Every customer is a new stop (even if same address/location).
· 1 &endash; Each Customer Location ID is a new stop (even if same address/location). For example, if a customer has two deliveries, then this is classed as 1 stop.
· 2 &endash; Each Unique address/location is a new stop (even if Location ID is different).
· 3 &endash; Jobs/Customers that fall within the Resource MinTravelDistanceInFeet setting are considered the same stop (Default MinTravelDistanceInFeet = 150 unless explicitly set in Resource table).
The default value is zero (0).
Ü Note&emdash; Use this option if you have a lot of deliveries to the same stop. If you set service duration in the database and have a lot of stops in the same place, then your timing could be inaccurate.
Resource Recharge &endash; Enable recharge or redispatch for the schedule.
Bulk Recharge &endash; Instructs RMPI to use incoming actual measures data from Descartes Mobile to calculate recharges forward for single-ended jobs.
Max Recharge Depots to Try - Speeds up optimizations. RMPI only considers the closest recharging sites based on this value.
Pre Routing - Determines if pre-routing is used. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer uses pre-routing. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer does not use pre-routing.
The default value is true (checked).
Ü Note&emdash; Pre-routing reuses routes that it has made before. It makes the process of assignment quicker, but it also might give you slightly less accurate routes. However, it is recommended that it is turned on (checked). It should only be set to false (unchecked), if the cache file contains all (or the vast majority) of the required road distances. In this case, pre-routing slows optimization slightly wasting time determining that no routings are needed.
Route Exchange - Determines if the Optimizer will attempt to swap routes between resources. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer will attempt to swap entire routes between any pair of eligible resources (in accordance with zone files, capabilities, etc.). This is useful when resources have different cost structures (such as different driver pay), or are based at different depots. If the box is unchecked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will attempt to swap entire routes.
The default value is false (unchecked).
Auto Calculate Profile Cost &endash; Allows the system to calculate costs of routes based on Cost Profiles.
Measure Limits on Locations &endash; When enabled, performs a capacity check at each delivery location to ensure weight and security restrictions are met.
Route as Straight Truck &endash; When enabled, sets to Straight Truck, overriding the resource setting
Apply Master Routes &endash; When enabled, the system will attempt to assign unassigned orders to routes generated from master routes before assignment to other routes
Seed
Seeding routes is the process of identifying the difficult jobs (jobs with tight constraints), and assigning them before the easier jobs.

Zoned Orders - Determines if seeding is restriced to zoned jobs. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then it restricts seeding to zoned jobs. Un-zoned jobs are never used as seeds. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then it allows seeding with un-zoned jobs. The Optimizer will never seed with more than one un-zoned job in a single pass.
The default value is false (unchecked).
Ü Note&emdash; It is recommended that it should be set to true (checked) if all jobs are expected to be zoned. It should be set to false (unchecked) if there is a mix of zoned and un-zoned jobs.
Route &endash; Seeding routes is the process of identifying the difficult jobs (jobs with tight constraints), and assigning these jobs ahead of easier jobs. The Optimizer can then try to fill in around the difficult jobs.
Y: Optimizer seeds routes.
N: Optimizer does not seed routes.
Desired Areas - Enables improved handling for seeding with multiple depots. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), it prevents usable seeds from being assigned to the wrong area. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then it does not affect assignment.
The default value is true (checked).
Ü Note&emdash; This is especially useful in multi-depot settings where seed jobs might otherwise get assigned to a route with an inappropriate depot. Generally this should be set to true (checked), unless Assignment Process is producing bad answers.
Use
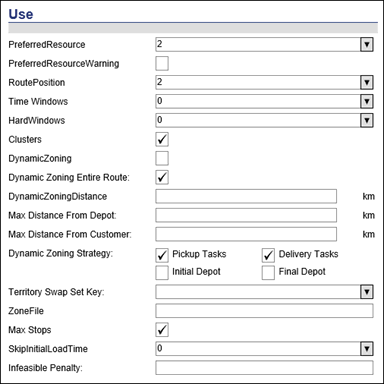
Preferred Resource - Determines the treatment of jobs’ RestrictPreferredRoute attributes. The valid values are:
· 0 &endash; Ignore jobs’ PreferredRoute attributes. Overrides jobs’ RestrictPreferredRoute attributes. It is equivalent to selecting all jobs and setting RestrictPreferredRoute to false (0).
· 1 &endash; Use jobs’ PreferredRoute attributes. Overrides jobs’ RestrictPreferredRoute attributes. It is equivalent to selecting all jobs and setting RestrictPreferredRoute to true (1).
· 2 &endash; Use PreferredRoute attributes on jobs that have RestrictPreferredRoute set to true (1).
The default value is to UsePreferredRoute default schedule setting.
Preferred Resource Warning - Determines whether a job that is not on a preferred resource is represented as a violation or a warning. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the job is displayed as a warning. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the job is displayed as a violation.
For baselines, have this option set to false (not checked) because you want jobs to saty on their set resource.
Route Position - Determines the treatment of tasks’ RoutePosition attributes and jobs’ Restrict[Type]RoutePosition attributes. The valid values are:
· 0 &endash; Ignore tasks’ RoutePosition attributes. Overrides jobs’ RestrictRoutePosition attributes. It is equivalent to selecting all jobs and setting RestrictRoutePosition to false (0).
· 1 &endash; Use tasks’ RoutePosition attributes. Overrides jobs’ RestrictRoutePosition attributes. It is equivalent to selecting all jobs and setting RestrictRoutePosition to true (1).
· 2 &endash; Use RoutePosition attributes on jobs that have RestrictRoutePosition set to true (1).
The default value is the RoutePosition default schedule setting.
Time Windows - Controls the application of a job and customer/depot time windows. The valid values are:
· 0 &endash; Apply any job time windows. Otherwise use customer/depot time windows.
· 1 &endash; Apply customer/depot time windows only. Ignore any job time windows.
· 2 &endash; Ignore all time windows. Only apply resource start and end times.
The default value is the TimeWindows default schedule setting.
Ü Note&emdash; This setting’s name may be misleading. This is not a Boolean attribute: a value of zero (0) does not turn time windows off, and a value of one (1) does not turn them on.
Hard Windows - Determines handling of Window LatestTime fields. The valid values are:
· 0 &endash; Job must be started by WindowLatestTime.
· 1 &endash; Job must be completed by WindowLatestTime.
· 2 &endash; Hancling is determined by the job’s Window Type attribute. If Window Type is zero (0), then the time window is arrival-based. If it is one (1), then the time window is completion-based.
The default value is the WindowLatestTime default schedule setting.
Ü Note&emdash; Use this setting when you have or need to have hard time windows. For example, if in your database you have a time window for a job between 12pm and 1pm, then with this setting, you can specify whether the job has to arrive by 1pm or be completed byt 1pm. If you have it set to option one (1), and the job is not completed by 1pm, then a violation is caused.
Clusters - Turns clustering on and off. Clustering encourages the Optimizer to assign jobs that are near each other on the same route. Nearness is decided by a number of factors. Two jobs for the same client at the same location are usually near, as are two jobs for clients across the street from each other. Using clustering can speed up the Assignment Process. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer attempts to keep jobs that are near to each other on the same route. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer does not cluster nearby jobs.
The default value is true (checked).
Ü Note&emdash; Clusters can be used only if there are no more than 65,535 jobs. Use AutoAssignCloseJobs to put all jobs for a single customer on the same route regardless of whether or not they will be served.
Ü Note&emdash; This is not really relevant in reservations, so it can be switched off. If you are using batch assignment, then it is recommended that it is switched on so that it can speed up the Assignment Process.
DynamicZoning &endash;Allows Optimizer to make appropriate geographic decisions based on the current set of orders in the system. Unlike "static" zones (which must be pre-determined in the data set using the "Zone" attributes), Dynamic Zoning allows the set of Resources/Jobs allowed for any given optimization to change over time based on the current assignment of jobs.
Dynamic Zoning Entire Route &endash; When Dynamic Zoning Entire Route is enabled, all the stops on a route as determined by the DynamicZoningStrategy setting must be within the DynamicZoningDistance value of each other. So if DynamicZoningStrategy is set to include pickup and dropoff stops and not Initial and Final Depots (default setting) then all the pickups and dropoffs must be within the DynamicZoningDistance of each other calculated straight line.
When Dynamic Zoning Entire Route is disabled, each stop on a route, as determined by the DynamicZoningStrategy setting, must be within the DynamicZoningDistance value of one other stop on the route. So if DynamicZoningStrategy is set to include pickup and dropoff stops and not Initial and Final Depots (default setting) then all the pickups and dropoffs must be within the DynamicZoningDistance of at least one other pickup or dropoff, calculated straight line.
DynamicZoningDistance &endash; Radius (in meters) around Job or Route that determines distance threshold for inclusion in DynamicZoning.
Max Distance from Depot &endash; Maximum as-the-crow-flies distance away from initial depot of resource.
Max Distance from Customer &endash; Maximum distance to path between any two customers. This setting only applies to customers using external pathing and is different from dynamic zoning. If both dynamic zoning and this setting are specified, the maximum distance between customers should be larger than the dynamic zoning distance; otherwise the optimizer will only plan routes for the lesser of the two.
Dynamic Zoning Strategy &endash; Applies dynamic zoning granularly to Pickup Tasks, Delivery Tasks, Initial Depot and/or Final Depot.
Territory Swap Set Key &endash; This field stores the name of the Territory Swap logic.
Zone File - Full path name of a file containing zone information. A zone file is a simple ASCII text file usually with a .lza file extension. You can use a zone file to define major and minor zones job zones.
A job zone is determined using the following precedence:
· The value in the job’s Zone attribute, if any.
· The Zone attribute on the customer record for the last task of the job:
|
Job Type |
Description |
Last Task |
|
0 |
Drop-off only |
Drop-off |
|
1 |
Pickup and Drop-off |
Drop-off |
|
2 |
Pickup only |
Pickup |
|
3 |
Multitask job |
Last task record in the job’s Task table |
The default value is the ZoneFile default schedule setting.
Ü Note&emdash; When you change the contents of the zone file, RIMMS does not read the changes until you either close and open the schedule, or:
1 Set ZoneFile to blank.
2 Set ZoneFile back to its original value.
3 Click on a route to update the route display.
Max Stops - Determines if RiMMS uses MaxStops when it optimizes the schedule. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then it uses the MaxStops attribute. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then it ignores the MaxStops attribute.
The default value is the MaxStops default schedule setting.
SkipInitialLoadTime &endash; With this option activated, double-ended orders will not incur any service duration when the pickup portion of the job takes place at the start of the route and at the initial depot of the resource, assuming the vehicle starts its route in a loaded state.
Infeasibility Penalty - Penalty only used in combination with the Infeasible constraints checked on in this section.
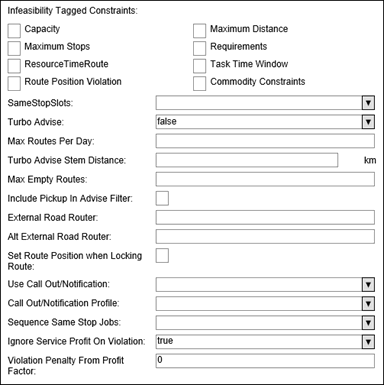
Infeasibility Tagged Constraints &endash; A string property that applies the ’Infeasible’ penalty when constraints fail. This features is designed to make some constraint violations less desirable, andsing this along with MinAssignmentProfit will prevent the assigner from generating routes with these constraint violations.
InfeasibilityTaggedConstraints can take a combination of the characters (C, D, S, R, T, W, Q, M). The following character codes will apply InfeasiblePenalty for:
• C - for Capacity
• D - for Maximum Distance
• S - for Maximum Stops
• R - for Requirements
• T - for Resource Time Window
• W - for Task Time Window
• Q &endash; Route Position Violation
• M - for Commodity Constraints
For example, an Infeasibility Tagged Constraints ’CR’ will apply the Infeasible penalty to a route stop if it is infeasible with respect to capacity constraint or requirements (C or R).
SameStopSlots &endash; Encourages the return of the same slots if there is already a stop in the same location as the requested advise
Turbo Advise &endash; Activates turbo advise functionality
Max Routes Per Day &endash; Maximum number of routes per day to be considered for turbo advise
Max Empty Routes &endash; If Max Empty Routes is set, the BGO can include up to this number of empty routes while searching for compatible used routes for batch assign.
Turbo Advise Stem Distance &endash; Radius from the order where available routes will be considered for turbo advise
External Road Router &endash; Map edit server URL used for RMPI routing. Please see the Precedence of External Router (Pather) URL section for more information.
Alt External Road Router &endash; Alternate map edit server URL used for RMPI routing. Please see the Precedence of External Router (Pather) URL section for more information.
Use Call Out/Notification &endash; Activate or deactivate Callouts/Notifications for this org
Call Out/Notification Profile &endash; This field will identify the primary key of the Callout/Notification Profile to use
Set Route Position when Locking Route &endash; Checkbox that sets route priority when locked.
Sequence Same Stop Jobs &endash; Configures the optimization sequence of multi-order stops:
• 0: Do not apply
• 1: Sequence deliveries before pickups by location key
• 2: Sequence deliveries first and then pickups by location key
Violation Penalty From Profit Factor (default value of 0.0): This field accepts a value between 0.0 and 1.0:
• When set to 0.0, no additional penalty is incurred (missed time window violations, excessive number of stops and stop order will each have their own penalty factors)
• When set to 1.0, all profit is added on as an additional penalty (missed time window violations, excessive number of stops or stop order will each have their own penalty factors)
• When set to 0.5, all profit is added as an additional penalty equal to half the task profit. Essentially, the profit for that stop increases by (1 - 0.5), multiplied by the task_profit.
Ignore Service Profit On Violation (default enabled): When enabled, regardless of the value of the Violation Penalty From Profit Factor field, violated stops will not contribute profit and no additional penalty is picked up other than missed time window violations, excessive number of stops or stop order issues. When disabled, the task profit is incurred completely for stops in violation.
Assignment
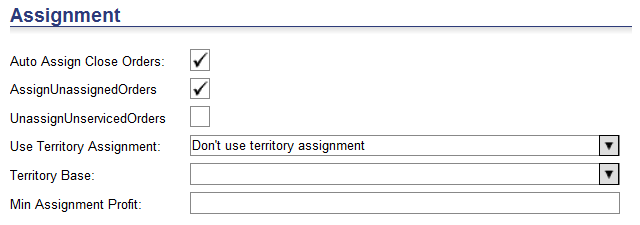
Auto Assign Orders - If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer attempts to assign orders to resources. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer does not run the Assignment Process.
Assign Unassigned Orders - If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then the Optimizer runs the Assignment Process and attempts to assign unassigned jobs to resources. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer does not run the Assignment Process and runs the Improvement Process only. It does not assign any of the remaining unassigned jobs.
Unassign Unserviced Orders - Determines if jobs that cannot be serviced are removed from routes. If the box is checked (true &endash; 1), then after the optimization is complete, the Optimizer will remove jobs that cannot be serviced leaving such jobs unassigned. If the box is not checked (false &endash; 0), then the Optimizer will not remove jobs that cannot be serviced.
The default value is false (not checked).
Ü Note&emdash; This option should be set to false (not checked) or you could end up with a lot of unassigned jobs.
Use Territory Assignment - Determines whether or not a Planner or Dispatcher can assign territories from the Unassigned Stops right-click menu.
· Do not use territory assignment &endash; the functionality will not be used.
· Automatically assign territory &endash; enables the Assign Territory right-click functionality and also allows Descartes Routing and Scheduling to automatically assign a territory when the order is created.
· Assign territory only when territory is null - enables the Assign Territory right-click functionality and also allows Descartes Routing and Scheduling to automatically assign a territory if the Territory field is null when creating the order.
Territory Base - Users can select one of the following options from this menu:
Base Territory on Delivery
Base Territory on Pickup
Base Territory on Location: When this option is selected, an additional drop-down menu appears with a description field, allowing users to select a City, Country, LocationKey, Postal Code and various UDF fields to define the territory. Use the operators used in the filters to match the value.
Min Assigned Profit &endash; Minimum incremental profit that a job must provide in order to be assigned. Number set too small may allow for job violations to be assigned. Number set too high will run longer and may lose potential negative net Job profit assignments, even when net Route profit is positive.
![]() Note&emdash;
A value of zero (0) will usually, but not always,
keep all unserved jobs from being assigned. Default value is -10000
Note&emdash;
A value of zero (0) will usually, but not always,
keep all unserved jobs from being assigned. Default value is -10000
Reservation Setting
Use Rmpi Advise - uses Rmpi for advice instead of adapi. It will give more precise return at the expense of performance.
Backhaul Dynamic Zoning Distance &endash; provides distance entry for advise calls with LastNStopForDZ values. If Backhaul Dynamic Zoning Distance is not configured per schedule, the configured CtySysValue equivalent is used. If the distance value entered is zero or is not configured anywhere in the system, backhaul dynamic zoning logic is not included in advise filter.
Pathing

Measure For Weight &endash; Select the Measure field you wish to use for weight
Measure To Weight Factor &endash; Enter the measure to weight factor
Dispatching
Start Route With GPS Message - if true (selected), a route will be considered dispatched when Routing and Scheduling receives a GPS message. If false (not selected), it needs a status message to dispatch the route.
Use AVL &endash; if true (selected), Routing and Scheduling will calculate AVL related fields after status/GPS messages.
On EndRoute &endash; This setting has the following values:
• 0 or null: Do not apply
• 1: Set missed to pending stops on End of Trip
• 2: Unassign pending stops on End of Trip. When set to 2, the system will unassign any pending or non-complete equivalent status stops of the route and then end the trip. This process will trigger a RMPI update.Update Planned Qty With Actual Pickup Qty &endash; Update planned measures with actual pickup measures
Update Planned Qty With Actual Pickup Qty &endash; Update planned measures with actual pickup measures
Set Static Recharge On Dispatch &endash; When this is true, all dynamic recharge will be converted to static recharge when dispatched
Set Actual Begun to Actual Arrived &endash; Sets the Actual Begun timestamp to Actual Arrived
BGO Freeze Window Size &endash; Using the time value (N) entered in this field, any improvement that would assign an order within the next ’N’ minutes will be rejected so as to avoid infeasible routes being created when running an execution BGO
BGO Min Stops to Freeze &endash; Using the stops value (N) entered in this field, any improvement that would assign an order to the next ’N’ stops will be rejected so as to avoid infeasible routes being created when running an execution BGO
BGO Allow Delivery Swap &endash; When enabled, this setting allows the BGO to swap orders between routes in an execution schedule.
Create Return on Miss &endash; With this setting is set to "1", when a stop is marked as ”Missed”, the system creates a new order, which moves goods from the customer back to the depot. With this setting set to ”r;2”, the system can handle cases where multi-task orders with two pickup tasks and a dropoff task would miss the second pickup and therefore the dropoff, making a return unnecessary.
• 0: Do not create Return on Miss
• 1: Create Return on Miss
• 2: Create Return on Miss only for double-ended orders.
Allow Partial Delivery &endash; When enabled, allows multi-task orders to be delivered even if one of the pickups is missed. This setting functions as follows when enabled:
• If one or more pickups are missed (but not all pickups) on a double-ended order, the system will allow drivers to complete the delivery of the pickups successfully completed.
• If the first pickup of a multi-task order is missed, the remaining pickups and their deliveries must remain in ”r;Pending” state.
• If the Return on Miss schedule setting is also enabled, if one pickup is missed, the rest of the tasks remain in ”r;Pending” status. If one delivery is missed, a return is created for completed pickups.
Please consider the following examples to illustrate this functionality.
Example 1:
• Return on Miss disabled
• Allow Partial Delivery disabled
• If one pickup is missed, then all other tasks are missed.
Example 2:
• Return on Miss disabled
• Allow Partial Delivery enabled
• If one pickup is missed, the rest of the tasks remain in ”Pending” status.
Example 3:
• Return on Miss enabled
• Allow Partial Delivery disabled
• If one pickup is missed, then all other tasks are missed. A return is created for completed pickups.
Example 4:
• Return on Miss enabled
• Allow Partial Delivery enabled
• If one pickup is missed, the rest of the tasks remain in ”Pending” status.
• If one delivery is missed, a return is created for completed pickups.
Set Time Window to Gen Time Window &endash; When this setting is enabled, the system will replace existing time windows with generated time windows based on projected arrival and projected departure values.
Lock Generated Time Window &endash; Locks generated time windows in place so that, when this setting is enabled, the system will return a violation if users attempt to update time windows for a route that fall outside the initial values.
Lock Generated Time Window &endash; Allowance X/Allowance Y &endash; allows users to round down the Projected Arrival Time value to the closest hour within a configurable time interval (X) and round up to the closest hour within another configurable time interval (Y).
For example:
If the Projected Arrival Time is 12:45 and the Projected Departure Time is 13:00, then X = 60 and Y = 60. The generated time windows in this case would be calculated as follows:
Projected Arrival Time: (12:45 - 00:60) = 11:45. When rounded down, the value becomes 11:00 hours.
Projected Departure Time: (13:00 + 00:60) = 14:00. When rounded up, the value remains 14:00 hours.
Lock Next Trip on Recharge Complete &endash; This setting has the following options:
• 0: disabled (default)
• 1: set route position as trip number
• 2: set route position as stop number
When this setting is enabled, the system will lock all other stops of the next trip, setting both the route position and preferred route.
This setting can be used to allow same-day execution of single-ended orders requiring the route to return to the depot prior to scheduling new work. To ensure this behavior occurs on the first trip, the route must be marked as "Start Empty", allowing a status at the initial recharge to limit the capacity of the remainder of the trip. This feature is useful for customers using reloads that do not work with a single commodity (e.g. Gas).
![]() Note&emdash;
The Lock Next Trip on Recharge Complete setting only applies to pickups
or deliveries. It will not be applied to double-ended or complex orders.
Note&emdash;
The Lock Next Trip on Recharge Complete setting only applies to pickups
or deliveries. It will not be applied to double-ended or complex orders.
![]() Note&emdash;
This configuration is only utilized if Use Route Position is configured
to ”r;1” or ”r;2”.
Note&emdash;
This configuration is only utilized if Use Route Position is configured
to ”r;1” or ”r;2”.
3rd Party Distance

Type - specifies the type of a schedule. Possible values are:
• Reservation
• Planning
• Execution
• Simulation
Only the Execution type can have status/GPS messages.
Reschedule Orders
Default Reschedule Key &endash; Default ScheduleKey when a reschedule is called without a destination ScheduleKey
Partial Completed - This field indicates whether or not to allow rescheduling of double or multi-task job orders when only a portion of this order has been completed. Choose one of the following from the drops down menu:
• Yes &endash; Allow rescheduling of orders that have been partially completed
• No &endash; Do not allow rescheduling on partially completed orders
Publish Configuration Settings
UseAutoPublish - This checkbox allows users to set this schedule to use the Autopublish routes functionality defined in the AVL parameters for this schedule.
Use Auto Publish Lock &endash; When enabled, this setting will lock the route when the autopublish command XML is sent from Descartes wGLN. By default, the Use Auto Publish Lock setting is disabled.
Use Schedule Publishing Settings &endash; Enable or disable the publish settings defined at the Schedule level. If disabled and the global setting is on, then it will use the global publishing settings.
Account Name - Account name for Autopublish functionality. This value will be included in the published xml.
Connection Type - Type of connection to publish data from Routing and Scheduling. The supported connection types are FTP, HTTP and Local Path.
Local Publish Path - If the connection type is Local Path, this field stores the directory path where files will be published.
Sender ID - This field holds the SenderID value to publish in the xml. Normally used to identify the place from which the data is sent.
Receiver ID - This field holds the ReceiverID value to publish in the xml. Normally used to identify the destination of the data.
Publish Configuration Settings
Straight Line Speed &endash; Value used when RMPI cannot find a legal road to navigate from one point to another (m/s)